OET - Occupational English Test
The Occupational English Test (OET): A Comprehensive Guide for Healthcare Professionals
The Occupational English Test (OET) is a unique and specialized English language exam designed specifically for healthcare professionals. Unlike general English exams, OET assesses English proficiency in the context of healthcare, focusing on the language skills required for real-life medical and professional settings. This exam is widely recognized by healthcare regulatory bodies, universities, and immigration departments across English-speaking countries, including the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, Ireland, and Singapore.
For those aspiring to work or study in the healthcare field in an English-speaking environment, OET provides a tailored, profession-specific assessment, making it the preferred choice over more general language tests like IELTS or TOEFL. On this page, we’ll explore what the OET entails, the test format, its advantages, and preparation tips.
What is the OET?
The Occupational English Test (OET) is a high-stakes language test developed by Cambridge Boxhill Language Assessment, a joint venture between Cambridge Assessment English and Box Hill Institute. Unlike other English proficiency exams, OET is designed specifically for 12 healthcare professions, including:
- Nursing
- Medicine
- Dentistry
- Pharmacy
- Physiotherapy
- Veterinary Science
- Speech Pathology
- Occupational Therapy
- Radiography
- Podiatry
- Optometry
- Dietetics
Each version of the OET is tailored to reflect the vocabulary, interactions, and situations relevant to each profession. This allows test-takers to demonstrate English proficiency in a context that matches their day-to-day responsibilities, making it more practical and meaningful for their future careers.
Why Choose the OET?
OET offers several unique benefits for healthcare professionals, which make it a preferred choice for those seeking to work, study, or migrate in the field of healthcare.
1. Professional Relevance
OET content is specific to the healthcare field, which means that test-takers encounter scenarios, language, and tasks that reflect real-life professional settings. For example, nurses might be asked to explain a medication's dosage to a patient, or doctors may need to understand a medical case history. This context-specific language evaluation helps candidates prove not only their English proficiency but also their ability to communicate effectively in healthcare settings.
2. Global Recognition
OET is recognized by numerous healthcare boards, councils, and immigration agencies around the world, including in the U.K., Australia, New Zealand, and several other countries. Successful OET results are accepted for visas, professional registration, and licensing, allowing candidates to pursue career opportunities in their chosen countries.
3. Targeted Skill Assessment
The test evaluates four main language skills—listening, reading, writing, and speaking—in healthcare-specific scenarios. For example, writing tasks are tailored to each profession and might involve creating a referral letter or a case summary. The speaking portion often involves role-plays that simulate real-life interactions between healthcare professionals and patients, providing a relevant and practical way to assess communication skills.
4. Improved Career Readiness
Since OET tests candidates in professional, healthcare-oriented scenarios, it helps ensure that they are better prepared to handle day-to-day responsibilities in English-speaking healthcare environments. This preparation goes beyond general language skills, focusing on situations they are likely to encounter in the workplace.
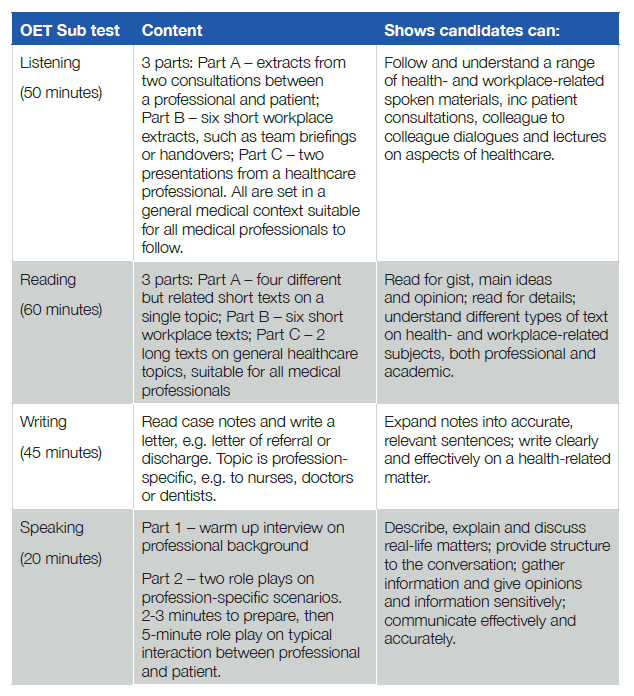
OET Test Format and Sections
The OET consists of four main sections, each designed to assess specific language skills within a healthcare context. Here’s a breakdown of each section:
1. Listening (Approximately 50 minutes)
The listening test has three parts, designed to evaluate comprehension of spoken English in a healthcare context:
- Part A: Consists of consultations between a healthcare professional and a patient. Candidates are required to complete notes based on the conversation.
- Part B: Features six short workplace-related extracts, such as team briefings or handovers, where candidates answer multiple-choice questions.
- Part C: Involves two longer audio extracts, often featuring an expert talking about healthcare topics, with multiple-choice questions following each.
2. Reading (60 minutes)
The reading section assesses the ability to understand written information relevant to healthcare professionals:
- Part A: A rapid-fire test where candidates must read and locate information across several short texts in 15 minutes.
- Part B: Comprises six multiple-choice questions related to short workplace extracts such as guidelines or policy documents.
- Part C: Involves reading two longer texts about healthcare topics and answering multiple-choice questions for each.
3. Writing (45 minutes)
In the writing section, candidates are asked to complete a task specific to their profession. For example, nurses may need to write a referral letter, while doctors might be asked to write a case summary or a discharge letter. The writing tasks evaluate the candidate's ability to communicate effectively in writing, including the use of appropriate tone, vocabulary, and structure for a healthcare setting.
4. Speaking (Approximately 20 minutes)
The speaking section involves two role-plays between the candidate and the interlocutor (playing the role of a patient or relative). Each role-play simulates a realistic healthcare scenario. For example, a dentist might explain post-treatment care to a patient, or a pharmacist might discuss medication instructions. This section tests candidates’ ability to communicate clearly, empathetically, and effectively in patient interactions.
Preparing for the OET: Tips and Resources
Preparation is key to success in OET, especially given the profession-specific content. Here are some useful tips and resources to help candidates prepare:
1. Understand the Test Format
Familiarize yourself with the structure and requirements of each section. Understanding the types of questions and tasks you’ll encounter can help reduce test anxiety and improve performance. Official OET preparation materials, including sample tests, can be extremely helpful.
2. Practice Healthcare-Specific Vocabulary
Since OET is a healthcare-specific exam, candidates should be comfortable with the terminology and phrases commonly used in their profession. Reading medical journals, attending seminars, or practicing with case studies in English can help improve familiarity with healthcare language.
3. Utilize Official OET Preparation Materials
OET offers a variety of official preparation resources, including online courses, sample tests, practice books, and a dedicated Preparation Portal. These resources provide an accurate representation of the test content and are invaluable for effective preparation.
4. Take Practice Tests
Simulating test conditions through practice tests helps candidates develop time management skills and build confidence. Practice tests can help candidates identify areas of improvement and get used to the pace and format of the actual test.
5. Seek Feedback
Enrolling in an OET preparation course or working with a tutor can provide valuable feedback on speaking and writing tasks. Professional guidance can help candidates refine their language skills and improve their test performance.
Registering for the OET
OET can be taken in test centers worldwide or as a remote test (OET@Home). To register, candidates need to create an OET account on the official website, select their test date and location, and complete the registration process. Test dates are available throughout the year, though availability may vary by location.
Who Recognizes the OET?
OET scores are widely recognized by healthcare regulatory bodies and immigration departments in many countries, making it a popular choice for those looking to study, work, or migrate in healthcare. Here are some organizations that recognize OET:
- In the U.K.: The Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC), General Medical Council (GMC), and the General Pharmaceutical Council.
- In Australia: The Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency (AHPRA) and Australian Department of Home Affairs for visa purposes.
- In New Zealand: The Medical Council of New Zealand (MCNZ) and the Nursing Council of New Zealand.
- In Ireland: Health and Social Care Professionals Council.
For many healthcare professionals, OET is a trusted and valuable asset in achieving their career and migration goals.
Conclusion
The Occupational English Test (OET) is a specialized, profession-oriented English test that serves as a bridge for healthcare professionals aiming to work, study, or migrate in English-speaking countries. Its focus on healthcare contexts makes it the preferred choice for professionals who need to prove their language proficiency in settings where effective communication with patients and colleagues is essential. With tailored content, global recognition, and comprehensive preparation resources, OET empowers healthcare professionals to pursue their careers confidently in new environments.
Whether you're a nurse, doctor, pharmacist, or other healthcare professional, OET provides a pathway to fulfilling your career aspirations and making a difference in global healthcare.
OET Test Format - Chart